Air Cooled Condenser: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Function and Benefits
Air Cooled Condenser: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Function and Benefits
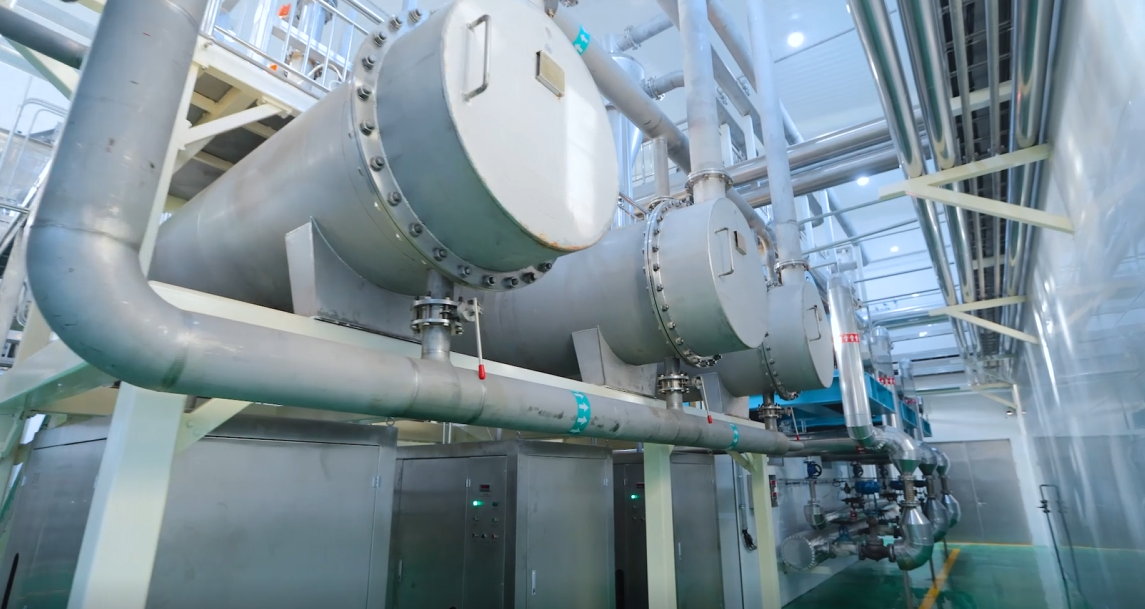
An air-cooled condenser is a type of heat exchanger that is used to cool and condense steam from a power plant’s steam turbine. It is an essential component of a power plant’s cooling system and is designed to remove heat from the steam by transferring it to the surrounding air. The condenser works by using a network of tubes to circulate the steam through a series of fins, which are exposed to the air.

One of the main advantages of an air-cooled condenser is that it does not require a constant source of water, unlike other types of condensers. This makes it particularly useful in areas where water is scarce or expensive. Additionally, air-cooled condensers are more environmentally friendly than water-cooled condensers, as they do not release heated water back into the environment, which can have a negative impact on local ecosystems.
Overall, air-cooled condensers are a reliable and efficient way to cool and condense steam in power plants. They offer a number of benefits over other types of condensers, including lower water usage and reduced environmental impact. As such, they are an important component of modern power plant cooling systems.
Design Principles

Air-cooled condensers are an important component of many cooling systems. They are designed to transfer heat from the refrigerant to the surrounding air. The design principles of air-cooled condensers are critical to ensuring their efficiency and effectiveness.
Heat Transfer Efficiency
The heat transfer efficiency of an air-cooled condenser is determined by several factors, including the surface area of the condenser, the Vacuum Pump Unit type of fins used, and the air flow rate. The surface area of the condenser is determined by the size of the unit and the number of tubes or fins used. The type of fins used can also impact heat transfer efficiency. For example, a condenser with spiral fins will have a higher heat transfer coefficient than one with plain fins.
The air flow rate is also critical to heat transfer efficiency. A higher air flow rate will result in better heat transfer, but it can also increase the noise level of the unit. The design of the air flow path is important to ensure that air is evenly distributed across the entire surface of the condenser.
Air Flow Dynamics
The air flow dynamics of an air-cooled condenser are also critical to its efficiency. The air flow path must be designed to ensure that air flows evenly across the entire surface of the condenser. This can be achieved through the use of baffles or other flow control devices. The design of the fan blades is also important to ensure that air is moved efficiently across the condenser.
The placement of the air-cooled condenser within the cooling system is also important. It should be located in an area where it can receive adequate airflow without being obstructed by other components. This will help to ensure that the condenser operates at maximum efficiency.
In conclusion, the design principles of air-cooled condensers are critical to their efficiency and effectiveness. By considering factors such as heat transfer efficiency and air flow dynamics, designers can create units that are both efficient and reliable.
Types of Air Cooled Condensers

Air cooled condensers are widely used in various industries to remove heat from the refrigerant. There are two main types of air cooled condensers: forced draft and induced draft.
Forced Draft
In a forced draft air cooled condenser, the fan is located at the air inlet side of the condenser. The fan forces the air through the condenser coil, which helps to increase the heat transfer rate. This type of condenser is generally used in applications where the ambient air temperature is high.
Induced Draft
In an induced draft air cooled condenser, the fan is located at the air outlet side of the condenser. The fan pulls the air through the condenser coil, which creates a negative pressure at the air inlet side of the condenser. This helps to increase the heat transfer rate. This type of condenser is generally used in applications where the ambient air temperature is low.
Overall, the type of air cooled condenser used depends on the specific application and the environmental conditions. Forced draft air cooled condensers are more commonly used in high temperature environments, while induced draft air cooled condensers are more commonly used in low temperature environments.
Operational Mechanics

Refrigerant Cycle
Air-cooled condensers are used in refrigeration systems to remove heat from the refrigerant. The refrigerant cycle begins with the compressor compressing the refrigerant gas to a high pressure and temperature. The high-pressure gas then passes through the condenser where it is cooled by the ambient air flowing over the condenser coils. As the refrigerant is cooled, it condenses back into a liquid state.
The condensed liquid refrigerant then flows through the expansion valve, where it is allowed to expand and cool. The now cold and low-pressure refrigerant then flows through the evaporator, where it absorbs heat from the surrounding air or objects and turns back into a gas. The gas then returns to the compressor to start the cycle again.
Temperature Control
The temperature control of an air-cooled condenser is important to ensure the proper operation of the refrigeration system. The condenser fan motor and the compressor are controlled by a thermostat that monitors the temperature of the refrigerant leaving the condenser.
If the refrigerant temperature rises above the set point, the thermostat will turn on the condenser fan motor to increase the airflow over the condenser coils. This increased airflow will help to remove more heat from the refrigerant, lowering its temperature.
If the refrigerant temperature continues to rise, the thermostat will also turn on the compressor to increase the refrigerant flow rate and remove more heat from the system. This temperature control system ensures that the refrigeration system operates efficiently and reliably.
Material Considerations
Corrosion Resistance
When selecting materials for an air-cooled condenser, corrosion resistance is a critical consideration. The condenser will be exposed to various elements, including moisture, heat, and potentially corrosive chemicals. Therefore, the materials used must be resistant to corrosion to ensure the longevity and efficiency of the condenser.
Some common materials used for air-cooled condensers include stainless steel, aluminum, and copper. Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and is often used in harsh environments. Aluminum is lightweight and also has excellent corrosion resistance. Copper is an excellent conductor of heat and has good corrosion resistance, but it is more expensive than aluminum.
Thermal Conductivity
Another critical consideration when selecting materials for an air-cooled condenser is thermal conductivity. The materials used must be able to efficiently transfer heat from the refrigerant to the air to ensure the condenser’s optimal performance.
Copper is an excellent conductor of heat and is often used in high-performance air-cooled condensers. Aluminum also has good thermal conductivity and is often used in lower-cost condensers. Stainless steel has lower thermal conductivity than copper and aluminum, but it is still a viable option for certain applications.
In conclusion, selecting the right materials for an air-cooled condenser is critical to ensure its longevity and optimal performance. The materials must be resistant to corrosion and have good thermal conductivity. Stainless steel, aluminum, and copper are common materials used in air-cooled condensers, each with their own advantages and disadvantages.
Installation and Siting
Space Requirements
When installing an air-cooled condenser, it is important to consider the space requirements. The unit should be placed on a flat, stable surface that can support its weight and the weight of any additional equipment that may be installed. The condenser should also be positioned in such a way that it has adequate clearance on all sides for maintenance and repair work.
The amount of space required will depend on the size of the unit, as well as any additional equipment that may be installed, such as fans or pumps. It is important to consult the manufacturer’s specifications to determine the exact space requirements for a particular unit.
Environmental Impact
The installation and siting of an air-cooled condenser can have an impact on the environment. It is important to consider factors such as noise pollution and the potential for air pollution.
To minimize noise pollution, the condenser should be placed away from residential areas and sensitive environments such as hospitals and schools. The use of noise barriers or acoustic enclosures may also be necessary in some cases.
The potential for air pollution can be minimized by ensuring that the condenser is located away from sources of dust and other pollutants. Regular maintenance and cleaning of the unit can also help to reduce the risk of air pollution.
Overall, careful consideration of the space requirements and environmental impact of an air-cooled condenser is essential to ensure that the unit operates efficiently and effectively while minimizing its impact on the surrounding environment.
Maintenance and Servicing
Cleaning Procedures
Regular cleaning of the air cooled condenser is essential to maintain its efficiency and prolong its lifespan. The cleaning frequency depends on the operating environment, but it is recommended to clean the condenser at least once a year. The following steps should be followed for effective cleaning:
- Turn off the power supply to the condenser.
- Remove any debris or leaves from the fins using a soft brush.
- Use a pressure washer to remove any dirt or grime from the fins. Ensure that the pressure is not too high as this can damage the fins.
- Clean the fan blades using a soft brush or cloth.
- Check the drain pan for any debris and clean if necessary.
- Turn on the power supply and check the condenser for any leaks.
Wear and Tear Monitoring
Regular monitoring of the air cooled condenser is important to identify any signs of wear and tear. The following components should be checked regularly:
- Fins: Check for any signs of damage or corrosion. Replace any damaged fins to maintain the efficiency of the condenser.
- Fan blades: Check for any signs of wear or damage. Replace any damaged blades to prevent any imbalance that can cause damage to the motor.
- Motor: Check for any signs of wear or damage. Lubricate the motor if necessary.
- Electrical connections: Check for any loose or corroded connections. Tighten or replace any damaged connections to prevent any electrical faults.
By following these maintenance and servicing procedures, the air cooled condenser can operate efficiently and effectively for many years.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Energy Saving Technologies
Air-cooled condensers are designed to provide high energy efficiency and sustainability. The latest air-cooled condensers are equipped with advanced technologies that enhance energy efficiency. One such technology is variable speed drives (VSDs) that help to reduce energy consumption by adjusting the fan speed according to the cooling needs. This technology ensures that the system operates at optimal levels, which reduces energy consumption and costs.
Another technology that is gaining popularity is the use of microchannel coils. These coils have smaller tubes and fins, which increase heat transfer efficiency and reduce the amount of refrigerant needed. This technology also reduces the size and weight of the air-cooled condenser, making it more compact and easier to install.
Regulatory Compliance
Air-cooled condensers are designed to comply with various regulations and standards that promote sustainability. For instance, the European Union has set strict regulations on the use of refrigerants that contribute to global warming. Air-cooled condensers are designed to use refrigerants that have low global warming potential (GWP) and comply with the EU F-Gas regulation.
In addition, air-cooled condensers are designed to comply with energy efficiency standards such as the Energy Star rating. This rating system ensures that the air-cooled condenser meets the minimum energy efficiency requirements, which reduces energy consumption and costs.
Overall, air-cooled condensers are a sustainable and energy-efficient solution for cooling needs. With advanced technologies and regulatory compliance, these systems provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for various applications.
Applications
Air-cooled condensers are widely used in various industries and HVAC systems. This section discusses the applications of air-cooled condensers in industrial cooling and HVAC systems.
Industrial Cooling
Air-cooled condensers are commonly used in industrial cooling applications where water is scarce or expensive. They are ideal for cooling large volumes of water or other fluids in industrial processes. The condenser’s ability to cool fluids at high temperatures makes them suitable for use in power plants, chemical plants, refineries, and other industrial facilities.
In the power generation industry, air-cooled condensers are used to cool the steam that is used to generate electricity. They are also used in the oil and gas industry to cool the fluids used in drilling and production processes. Other industries that use air-cooled condensers include food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing.
HVAC Systems
Air-cooled condensers are also commonly used in HVAC systems. They are used to cool the refrigerant in air conditioning systems, which in turn cools the air that is circulated throughout a building. Air-cooled condensers are commonly found in small to medium-sized commercial buildings, such as offices, retail stores, and restaurants.
One of the advantages of air-cooled condensers in HVAC systems is that they do not require water to operate, which makes them ideal for use in areas where water is scarce or expensive. They are also easy to install and maintain, which makes them a popular choice for building owners and facility managers.
In conclusion, air-cooled condensers are versatile and widely used in various industries and HVAC systems. They offer several advantages, including high efficiency, low maintenance, and no water requirements, making them an attractive choice for many applications.
Innovations in Air Cooled Condensers
Advancements in Design
Air cooled condensers have been used in the HVAC industry for decades, but recent advancements in design have improved their efficiency and effectiveness. One of the most significant innovations in air cooled condensers is the use of microchannel technology. This technology allows for a more compact design, which reduces the overall size and weight of the unit. Additionally, microchannel coils have a higher heat transfer rate, which results in improved efficiency and performance.
Another advancement in design is the use of variable speed fans. Traditional air cooled condensers have fixed speed fans, which can be inefficient and noisy. Variable speed fans adjust their speed based on the cooling load, resulting in improved energy efficiency and reduced noise levels.
Smart Control Systems
Smart control systems have revolutionized the way air cooled condensers are operated and maintained. These systems use sensors and algorithms to monitor and optimize the performance of the unit. They can detect issues before they become major problems, and can even predict when maintenance is required.
One example of a smart control system is the use of predictive maintenance. This system uses data from sensors to predict when components are likely to fail, allowing for proactive maintenance before a breakdown occurs. This can reduce downtime and maintenance costs, and extend the life of the unit.
Another example is the use of remote monitoring. Smart control systems can be accessed remotely, allowing technicians to diagnose and troubleshoot issues without having to be on site. This can save time and money, and can improve the overall reliability of the unit.
In conclusion, innovations in air cooled condensers have improved their efficiency, effectiveness, and reliability. Advancements in design, such as microchannel technology and variable speed fans, have resulted in improved performance and reduced energy consumption. Smart control systems, including predictive maintenance and remote monitoring, have made it easier to operate and maintain air cooled condensers.
Market Trends
Consumer Demand
Air cooled condensers are becoming increasingly popular in the market due to their energy efficiency and low maintenance costs. Consumers are looking for cost-effective and eco-friendly solutions for their cooling needs, and air cooled condensers fit the bill perfectly. They are easy to install and require minimal maintenance, making them a popular choice among consumers.
Moreover, air cooled condensers are highly versatile and can be used in a wide range of applications, including HVAC systems, refrigeration units, and power plants. This versatility has further contributed to their growing popularity among consumers.
Technological Developments
The air cooled condenser market is witnessing significant technological advancements, which are aimed at improving their efficiency and performance. Manufacturers are investing in research and development to introduce new and innovative products that can meet the evolving needs of consumers.
For instance, some manufacturers are developing air cooled condensers with advanced control systems that can optimize their performance based on the specific cooling requirements. These systems can automatically adjust the fan speed, airflow, and other parameters to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency.
In addition, some manufacturers are using advanced materials and coatings to improve the durability and corrosion resistance of air cooled condensers. This can extend their lifespan and reduce maintenance costs over the long term.
Overall, the air cooled condenser market is expected to witness steady growth in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient and eco-friendly cooling solutions. With ongoing technological advancements and innovations, air cooled condensers are likely to remain a popular choice among consumers for their cooling needs.
Future Outlook
Research Directions
As air-cooled condensers continue to gain popularity in various industrial applications, research and development efforts are expected to focus on enhancing their efficiency and reliability. One area of interest is the use of advanced materials and coatings to improve heat transfer and corrosion resistance. Researchers are also exploring the potential of incorporating smart sensors and control systems to optimize the performance of air-cooled condensers and reduce energy consumption.
Another research direction is the development of hybrid cooling systems that combine air-cooled and water-cooled technologies. This approach can provide the benefits of both systems while minimizing their drawbacks, such as water scarcity and air fouling. Hybrid systems can also offer greater flexibility in adapting to changing environmental conditions and operating requirements.
Potential Growth Areas
The demand for air-cooled condensers is expected to grow in several industries, including power generation, petrochemicals, and refrigeration. In the power generation sector, air-cooled condensers are becoming increasingly popular as a replacement for water-cooled systems, especially in regions with water scarcity or strict environmental regulations. The petrochemical industry is also adopting air-cooled condensers to reduce water consumption and improve safety.
In the refrigeration industry, air-cooled condensers are used in a variety of applications, such as food processing, cold storage, and air conditioning. With the growing demand for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly refrigeration systems, air-cooled condensers are expected to play a significant role in the future.
Overall, the future outlook for air-cooled condensers is positive, with ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving their performance and expanding their applications. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability and efficiency, air-cooled condensers are likely to become an increasingly important component of their operations.