Feather Meal: An Overview of Its Production and Uses
Feather Meal: An Overview of Its Production and Uses
Feather meal is a byproduct of the poultry industry that is gaining popularity as a source of protein for animal feed. It is made by grinding up the feathers of chickens, turkeys, and other poultry into a fine powder, which is then processed to remove any remaining fat and moisture. The resulting product is a high-protein, low-fat ingredient that can be used in a variety of animal feed formulations.

One of the main advantages of feather meal is its high protein content. According to industry estimates, feather meal typically contains between 80 and 85 percent protein, making it one of the most concentrated sources of protein available for animal feed. This makes it an attractive option for farmers and feed manufacturers looking to boost the protein content of their feed formulations without adding excess fat or other unwanted nutrients.
Despite its many benefits, feather meal is not without its drawbacks. One of the main concerns surrounding this ingredient is its potential to harbor harmful bacteria, such as Salmonella and E. coli. To mitigate this risk, it is important to ensure that feather meal is properly processed and stored, and that it is included in animal feed formulations at appropriate levels.
Composition of Feather Meal

Feather meal is a byproduct of the poultry industry that is derived from poultry feathers. The composition of feather meal can vary depending on several factors, including the type of bird, the age of the bird, and the processing method used.
Feather meal is primarily composed of protein, with a typical protein content ranging from 80-85%. It is also a good source of essential amino acids, particularly cysteine and methionine. In addition to protein, feather meal contains a small amount of fat and ash.
One potential concern with feather meal is its low digestibility. This is due to the high levels of keratin, a structural protein found in feathers, which is resistant to digestion. However, processing methods such as hydrolysis and autoclaving can improve the digestibility of feather meal.
In terms of micronutrient content, feather meal is a good source of nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. It also contains smaller amounts of other essential nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and iron.
Overall, feather meal is a valuable source of protein and nutrients for use in animal feed and fertilizer. However, its low digestibility and variability in composition should be taken into consideration when formulating diets or fertilizer blends.
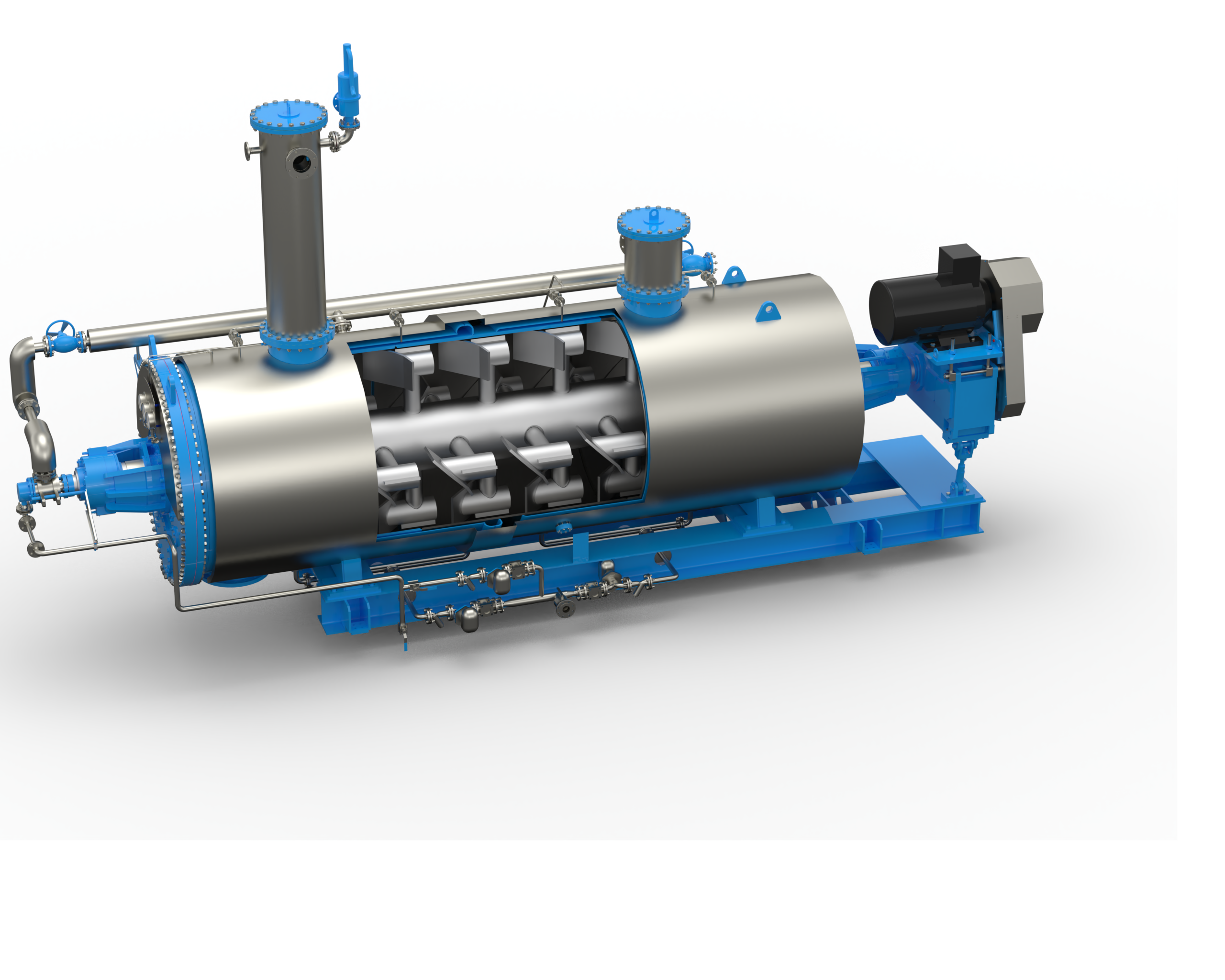
Production Process
Sourcing of Feathers
Feather meal is a byproduct of poultry processing, which is obtained from the feathers of chicken, ducks, turkeys, and other birds. The feathers are collected from poultry processing plants and then transported to feather meal processing facilities. The feathers are sourced from reputable and reliable suppliers to ensure that they are of high quality and free from contaminants.
Feather Cleaning and Sterilization
Once the feathers have been sourced, they are cleaned and sterilized to remove any dirt, bacteria, or other contaminants. The feathers are first washed with water to remove any dirt or debris. Then, they are sterilized using high-pressure steam to kill any bacteria or pathogens that may be present.
Feather Hydrolysis
After the feathers have been cleaned and sterilized, they are hydrolyzed to break down the protein into smaller peptides and amino acids. This process involves the use of high-pressure steam and high temperatures to break the protein bonds in the feathers. The resulting product is a brown, powdery substance that is rich in protein and amino acids.
Drying and Grinding
The hydrolyzed feather meal is then dried and ground into a fine powder. The drying process involves the use of hot air to remove any remaining moisture from the feather meal. The dried feather meal is then ground into a fine powder using specialized equipment.
In conclusion, the production process of feather meal involves sourcing feathers from poultry processing plants, cleaning and sterilizing the feathers, hydrolyzing the feathers to break down the protein, and drying and grinding the resulting product into a fine powder. This process ensures that the feather meal is of high quality and free from contaminants.
Nutritional Profile

Protein Content
Feather meal is a byproduct of the poultry industry that is made from ground-up feathers. It is a good source of protein, containing around 80-85% protein by weight. This makes it a useful ingredient in animal feed, as it can help to meet the protein requirements of animals such as chickens, pigs, and fish.
Amino Acid Composition
Feather meal is also a good source of amino acids, which are the building blocks of protein. It contains all of the essential amino acids that animals need to obtain from their diet, as well as a range of non-essential amino acids. The amino acid composition of feather meal can vary depending on the source of the feathers and the processing method used.
Mineral Content
In addition to protein and amino acids, feather meal also contains a range of minerals. These include calcium, phosphorus, and potassium, as well as smaller amounts of other minerals such as iron and zinc. The mineral content of feather meal can also vary depending on the source of the feathers and the processing method used.
Overall, feather meal is a useful ingredient in animal feed due to its high protein content and amino acid composition. Its mineral content can also provide additional nutritional benefits to animals. However, it is important to note that feather meal should not be the sole source of protein in an animal’s diet, as it may not provide all of the necessary nutrients in sufficient quantities.
Applications in Animal Feed
Poultry Feed
Feather meal is a valuable ingredient in poultry feed due to its high protein content and digestibility. It is commonly used as a source of amino acids, particularly methionine, which is essential for the growth and development of chickens. Feather meal is also rich in cysteine, which plays an important role in the formation of feathers and skin. In addition to its nutritional benefits, feather meal can improve the texture and palatability of poultry feed.
Aquaculture Feed
Feather meal is also used as a protein source in aquaculture feed. It is particularly useful in the production of fish feed due to its high protein content and digestibility. Feather meal can be used to replace other protein sources, such as fish meal, which can be expensive and limited in availability. In addition, feather meal can improve the growth and feed conversion rates of fish.
Ruminant Feed
Feather meal can also be used in ruminant feed, although it is less commonly used than in poultry and aquaculture feed. It can be a valuable source of protein for ruminants, particularly in situations where other protein sources are limited. Feather meal can also improve the digestibility of other feed ingredients, such as corn and soybean meal.
Overall, feather meal is a versatile ingredient in animal feed, providing a valuable source of protein and improving the nutritional value of feed. However, it is important to ensure that feather meal is properly processed and free from contaminants to ensure the safety and health of animals consuming it.
Environmental Impact
Waste Reduction
Feather meal is a byproduct of poultry processing, and its production can lead to a reduction in waste. The feathers that are used to make feather meal would otherwise be disposed of as waste, which could lead to environmental concerns. By using these feathers to make feather meal, the amount of waste generated by the poultry industry can be reduced.
Emissions from Production
The production of feather meal can result in emissions of greenhouse gases and other pollutants. However, compared to other animal feed ingredients, feather meal has a relatively low environmental impact.
According to a study by the European Commission, feather meal has a carbon footprint that is lower than that of soybean meal, fish meal, and rapeseed meal. The study also found that feather meal had lower emissions of nitrogen and phosphorus than other animal feed ingredients.
Overall, while the production of feather meal does result in some emissions, its environmental impact is relatively low compared to other animal feed ingredients.
Regulatory Aspects
Quality Standards
Feather meal is a byproduct of poultry processing and is regulated by the Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO) in the United States. The AAFCO has established guidelines for the minimum protein content and maximum moisture content of feather meal. The minimum protein content is set at 80%, and the maximum moisture content is set at 12%.
In addition to protein and moisture content, the AAFCO also sets standards for ash content, which should not exceed 35%, and crude fat content, which should be less than 3%. These quality standards are important to ensure that feather meal is a safe and nutritious ingredient for animal feed.
Labeling Requirements
Feather meal is considered a feed ingredient and must be labeled accordingly. The label must include the name of the product, the net weight, and the name and address of the manufacturer or distributor. Additionally, the label must include a guaranteed analysis that lists the minimum protein content and maximum moisture content.
It is important to note that feather meal is not approved for use in organic livestock production. Therefore, if a product is labeled as “organic,” it cannot contain feather meals as an ingredient.
Overall, regulatory standards and labeling requirements for feather meals help ensure that it is a safe and reliable ingredient for animal feed.
Market Trends
Demand Dynamics
Feather meal is a byproduct of the poultry industry and is used as a source of protein in animal feed. The demand for feather meal is primarily driven by the growth in the animal feed industry. With the increase in global population and the rise in demand for meat products, the demand for animal feed is also expected to grow. This is expected to drive the demand for feather meals in the coming years.
Furthermore, the growing trend of organic and natural animal feed is expected to boost the demand for feather meals. Feather meal is a natural source of protein and is considered a sustainable alternative to synthetic protein sources. This is expected to increase the demand for feather meals in the organic and natural animal feed market.
Price Fluctuations
The price of feather meal is subject to fluctuations due to various factors such as the availability of raw materials, supply and demand dynamics, and production costs. The price of feather meal is also influenced by the price of other protein sources such as soybean meal and fish meal.
In recent years, the price of feather meas has been relatively stable due to the steady growth in demand and supply. However, the price of feather meals are expected to increase in the coming years due to the rise in demand and production costs.
Overall, the market for feather meals are expected to grow in the coming years due to the increasing demand for animal feed and the growing trend of natural and organic animal feed. However, the price of feather meals is expected to be subject to fluctuations due to various factors.
Storage and Handling
Shelf Life
Feather meals has a relatively long shelf life when stored properly. The shelf life of feather measl can vary depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to light. Generally, feather meals can be stored for up to 12 months without significant deterioration, provided that it is stored in appropriate conditions.
Storage Conditions
Feather meals should be stored in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area. It is important to protect feather meals from moisture, as moisture can cause the product to spoil or become moldy. Feather meals should also be protected from direct sunlight, as exposure to sunlight can cause the product to deteriorate.
It is recommended that feather meals be stored in sealed containers or bags to prevent moisture and air from entering. If stored in bulk, feather meals should be stored in a clean, dry, and well-maintained silo or bin.
When handling feather meals, it is important to wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and a dust mask. Feather meals can create dust, which can be irritating to the skin and respiratory system. It is also important to avoid contact with eyes and to wash hands thoroughly after handling feather meals.
Overall, proper storage and handling of feather meals are essential to maintaining its quality and shelf life. By following recommended storage and handling practices, users can ensure that feather meals remains a valuable and effective ingredient in animal feed and fertilizer formulations.
Challenges and Limitations
Potential Contaminants
Feather meals are produced by rendering feathers, which are a byproduct of the poultry industry. However, rendering can be a complex process and if not done correctly, it can lead to the presence of contaminants in the final product. Potential contaminants in feather meals may include heavy metals, pathogens, and residual veterinary drugs.
To ensure the safety of feather meals, it is important to source it from reputable suppliers who follow strict quality control measures. Additionally, testing for contaminants should be performed regularly to ensure that the product meets regulatory standards.
Allergenic Concerns
Feather meals are source of protein and can be used as an ingredient in animal feed. However, it is important to note that some animals may be allergic to feather meals. Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe and may include symptoms such as itching, swelling, and difficulty breathing.
To minimize the risk of allergic reactions, it is important to properly label products that contain feather meals and to avoid using it in formulations for animals that are known to be allergic. Additionally, proper storage and handling of feather meals can help prevent cross-contamination with other ingredients.
Overall, while feather meals has many benefits as a source of protein in animal feed, it is important to be aware of potential challenges and limitations associated with its use. By following proper sourcing, testing, labeling, and handling procedures, the risks associated with feather meals can be minimized.
Future Perspectives
Technological Advancements
Feather meals production has been a traditional process for many years, but with the advancement of technology, there is a possibility of improving the process. Several companies are exploring new ways to extract proteins from feathers more efficiently. One such method is the use of enzymes that can break down the feathers into smaller particles, which can then be processed further. This method not only increases the yield of protein but also reduces the production time.
Another technological advancement is the use of microwave technology, which can reduce the processing time of feather meals. The use of microwaves can break down the feathers faster and more efficiently than traditional methods, thereby increasing the yield of protein.
Sustainable Practices
The production of feather meals has been criticized for its environmental impact. However, there are several sustainable practices that can be adopted to reduce the environmental footprint of feather meals production.
One such practice is the use of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power to power the production process. This reduces the reliance on fossil fuels and reduces the carbon footprint of feather meals production.
Another sustainable practice is the use of organic solvents instead of harsh chemicals in the production process. This reduces the amount of toxic waste generated during the production process and makes the process more environmentally friendly.
In conclusion, the future of feather meals production looks promising with the adoption of new technologies and sustainable practices. These advancements not only increase the efficiency of the production process but also reduce the environmental impact of feather meals production.