Screw Conveyor: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Operation
Screw Conveyor: A Comprehensive Guide to Design and Operation
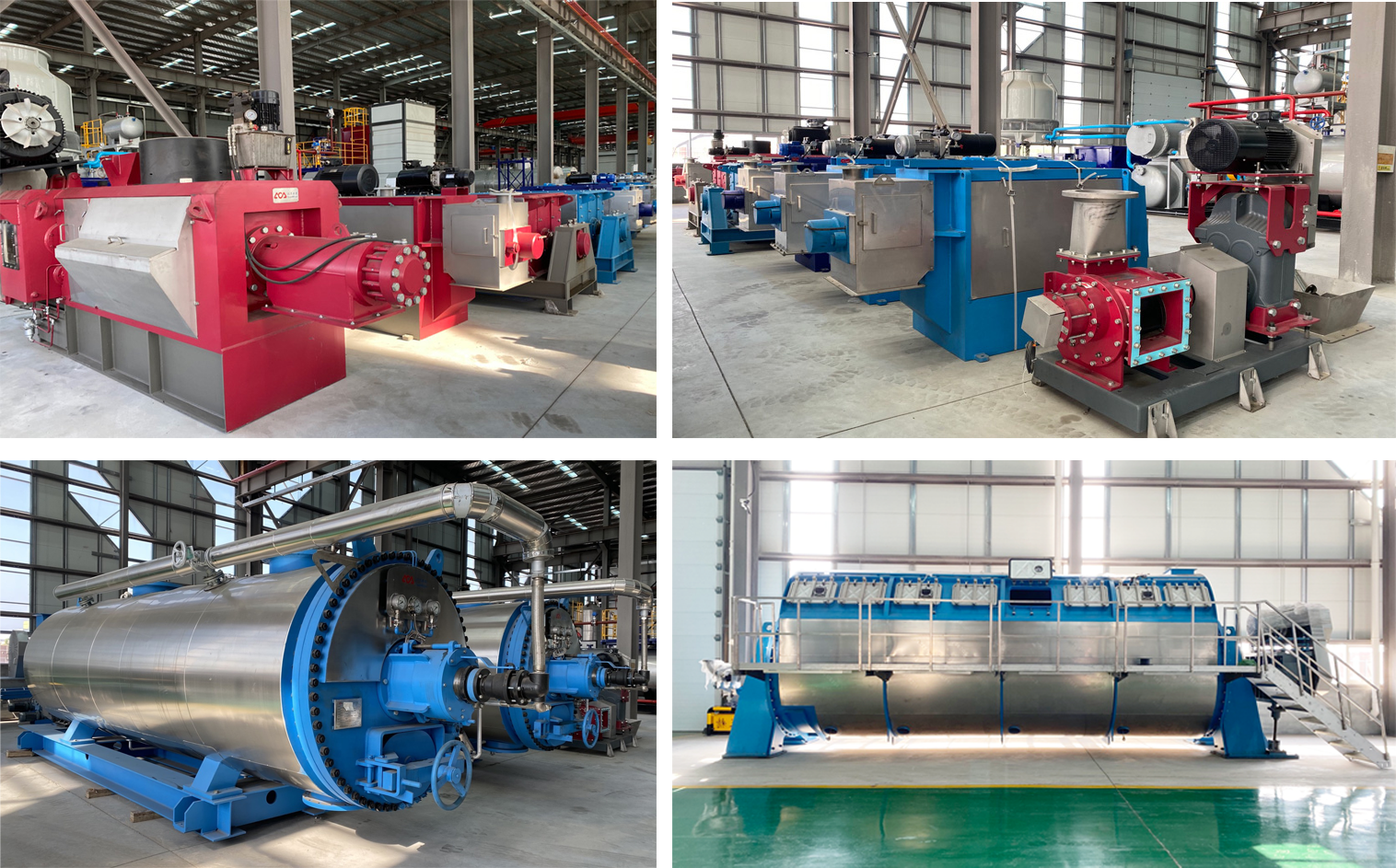
Screw conveyors are a type of mechanical conveyor that is commonly used to move bulk materials from one location to another. They are used in a variety of industries, including agriculture, food processing, mining, and construction. The basic design of a screw conveyor consists of a rotating helical screw blade that is enclosed within a tube or trough. As the screw rotates, it moves the material along the length of the conveyor.

One of the advantages of screw conveyors is their versatility. They can be used to move a wide range of materials, including powders, grains, and pellets. They can also be used to transport materials at various angles, including horizontal, vertical, and inclined. Additionally, screw conveyors can be customized to meet specific requirements, such as the length of the conveyor, the diameter of the screw, and the type of material being transported.
Another advantage of screw conveyors is their efficiency. They are able to move materials at a consistent rate, which can help to reduce processing times and improve overall productivity. Additionally, screw conveyors require minimal maintenance and are easy to clean, making them a cost-effective solution for many industries.
Design and Operation
Types of Screw Conveyors
Screw conveyors come in many different types, each designed to handle specific materials and applications. The most common types include horizontal screw conveyors, vertical screw conveyors, and inclined screw conveyors.
Horizontal screw conveyors are used to transport materials horizontally, while vertical screw conveyors are used to transport materials vertically. Inclined screw conveyors are used to transport materials at an angle. Each type of screw conveyor has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which type to use depends on the specific application.
Component Parts
Screw conveyors consist of several component parts, including the screw, trough, motor, and bearings. The screw is the main component of the conveyor and is responsible for moving the material. The trough is the surface on which the screw rotates and the material is transported. The motor provides the power to rotate the screw, and the bearings support the screw and reduce friction.
Design Considerations
When designing a screw conveyor, several factors must be considered, including the material being transported, the distance the material needs to travel, and the amount of material being transported. The size and shape of the screw, as well as the pitch and diameter, must also be carefully considered to ensure efficient and effective transport of the material.
Other design considerations include the type of motor to use, the type of bearings to use, and the type of trough to use. The material of construction must also be carefully considered, as different materials may be required depending on the type of material being transported and the environment in which the conveyor will be operating.
Overall, a well-designed screw conveyor can provide efficient and reliable transport of materials in a wide range of applications.
Applications and Uses

Industry Applications
Screw conveyors have a wide range of applications in various industries. They are commonly used in the food and beverage industry for conveying bulk materials such as grains, sugar, and coffee beans. In the chemical industry, screw conveyors are used for the transportation of powders, pellets, and granular materials. The pharmaceutical industry also uses screw conveyors for the handling of bulk drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Screw conveyors are also used in the construction industry for conveying cement, sand, and other building materials. The mining industry uses screw conveyors for the transportation of minerals and ores. The wastewater treatment industry also uses screw conveyors for the handling of sludge and other waste materials.
Material Handling
Screw conveyors are an efficient and cost-effective method of material handling. They can handle a wide range of materials, from powders and granules to sticky and abrasive materials. Screw conveyors can also be used for mixing, blending, and heating or cooling materials.
One of the advantages of screw conveyors is their ability to handle materials at any angle, from horizontal to vertical. They can also be designed to fit into tight spaces, making them ideal for use in small or confined areas.
Screw conveyors are also easy to maintain and operate. They require minimal maintenance and can be operated with a simple on/off switch or automated controls.
In summary, screw conveyors have a wide range of applications in various industries and are an efficient and cost-effective method of material handling.
Installation and Maintenance

Installation Procedures
Installing a screw conveyor requires careful planning and preparation. Before starting the installation process, it is important to ensure that the conveyor is compatible with the equipment it will be connected to and that it is appropriate for the materials it will be transporting.
The installation process involves several steps, including assembling the conveyor, connecting it to the equipment, and testing it to ensure that it is functioning properly. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully during each step of the installation process to avoid damaging the conveyor or causing safety hazards.
Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance is essential for ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of a screw conveyor. Regular maintenance should include inspecting the conveyor for signs of wear and tear, lubricating moving parts, and tightening any loose bolts or screws.
It is also important to regularly clean the conveyor to prevent the buildup of materials that could cause blockages or other issues. Additionally, any damaged or worn parts should be replaced promptly to avoid further damage to the conveyor.
Safety Guidelines
When installing or maintaining a screw conveyor, it is important to follow all relevant safety guidelines to avoid accidents or injuries. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses, and ensuring that the conveyor is properly secured and stable during installation or maintenance.
It is also important to avoid placing any body parts or clothing near moving parts of the conveyor and to disconnect the power source before performing any maintenance or repairs. By following these safety guidelines, operators can help ensure that the installation and maintenance process is completed safely and without incident.
Performance and Efficiency
Performance Metrics
Screw conveyors are known for their high efficiency in transporting bulk materials. The performance of a screw conveyor can be measured by several metrics, including throughput, power consumption, and material flow rate. Throughput is the amount of material that a screw conveyor can transport per unit of time. Power consumption is the amount of energy required to operate the screw conveyor. Material flow rate is the rate at which the material flows through the conveyor.
To optimize the performance of a screw conveyor, it is important to consider the specific requirements of the application. Factors such as the type of material being transported, the distance over which it needs to be transported, and the required throughput will all impact the performance of the conveyor.
Optimization Strategies
There are several strategies that can be used to optimize the performance of a screw conveyor. One approach is to use a larger diameter screw, which can increase the throughput of the conveyor. Another strategy is to adjust the pitch of the screw, which can impact the flow rate of the material.
In addition to these strategies, it is important to consider the design of the conveyor itself. The length and diameter of the conveyor, the angle of inclination, and the type of screw all play a role in determining the performance of the conveyor.
Overall, by carefully considering the specific requirements of the application and implementing appropriate optimization strategies, it is possible to achieve high levels of performance and efficiency with a screw conveyor.
Materials and Build Quality
Material Selection
The selection of materials for screw conveyors is crucial to ensure that the conveyor system is durable and can handle the materials being transported. The most commonly used materials for screw conveyors are carbon steel, stainless steel, and galvanized steel. Carbon steel is the most economical option and is suitable for non-corrosive materials. Stainless steel is more expensive but is ideal for corrosive materials and has a longer lifespan. Galvanized steel is also an option for corrosive materials but may not be suitable for high-temperature applications.
Other factors to consider when selecting materials include the size and shape of the screw, as well as the operating conditions such as temperature, humidity, and abrasiveness of the materials being transported.
Construction Standards
The build quality of screw conveyors is also critical to ensure that they are reliable and can operate efficiently. The construction standards for screw conveyors are set by industry organizations such as the Conveyor Equipment Manufacturers Association (CEMA) and the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME).
These standards specify the design, fabrication, and installation requirements for screw conveyors, including the materials used, the dimensions of the screw, and the tolerances for manufacturing. They also provide guidelines for the proper maintenance and operation of screw conveyors to ensure their longevity.
Overall, selecting the right materials and adhering to construction standards are essential to the quality and durability of screw conveyors. Proper maintenance and operation are also critical to ensure their longevity and efficient performance.



