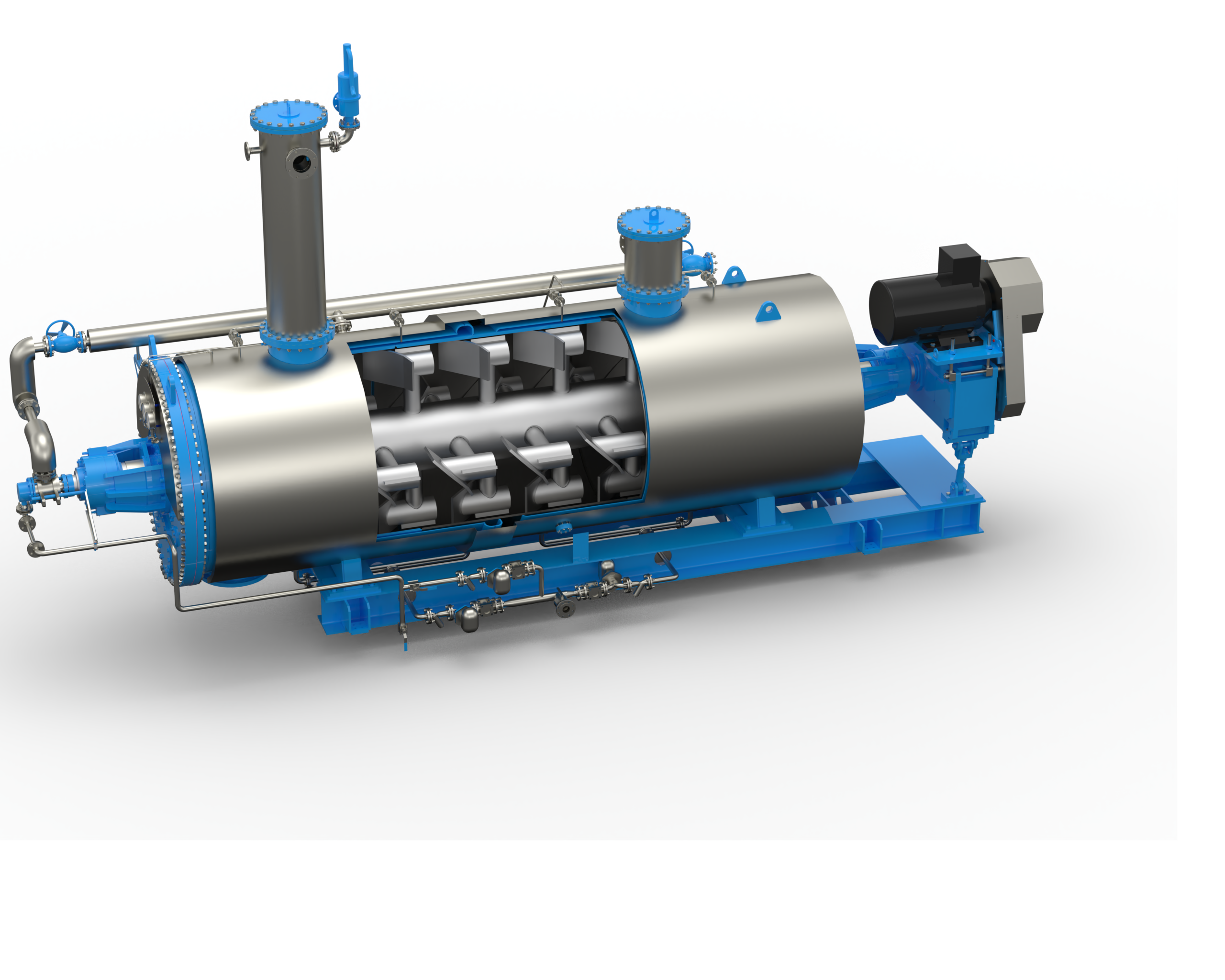
Fish Meal Plants: How They Work and Their Environmental Impact
Fish Meal Plants: How They Work and Their Environmental Impact
Fish meal plants are facilities that process fish into a high-protein feed ingredient used in animal feed. These plants play a critical role in the aquaculture and livestock industries, providing a valuable source of protein for animal nutrition. The process of producing fish meal involves cooking, pressing, drying, and grinding fish, resulting in a fine powder that is rich in protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and other essential nutrients.

Fish meal plants are typically located near fishing ports or fish processing facilities, where they can easily access raw materials. The production of fish meal is a complex process that requires specialized equipment and skilled workers. In addition to producing fish meal, some plants also produce fish oil, which is used in the production of dietary supplements and other products.
Overall, fish meal plants are an important component of the global food supply chain, providing a sustainable source of protein for animal feed. As demand for protein continues to grow, these plants will play an increasingly important role in meeting the nutritional needs of livestock and aquaculture industries.
Overview of Fish Meal Production
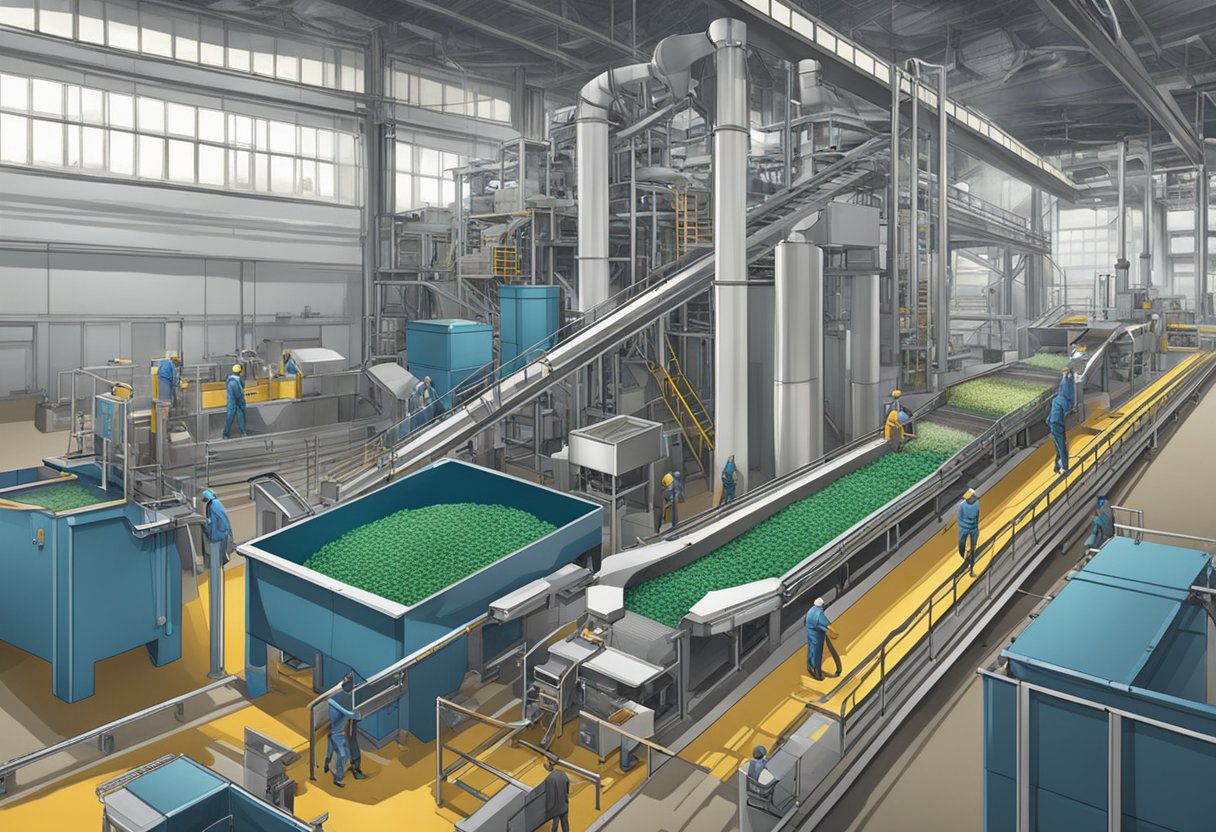

Process Flow
Fish meal is a high-protein supplement that is widely used in animal feed. The production of fish meal involves several stages, including cooking, pressing, drying, and grinding. The process begins with the collection of raw fish, which is then transported to the fish meal plant. At the plant, the fish is cooked in a steam cooker to break down the proteins and fats. The cooked fish is then pressed to remove the liquid, which is used to make fish oil. The solid material left behind is then dried in a dryer, which removes the remaining moisture. Finally, screw conveyor the dried material is ground into a fine powder, which is the finished fish meal product.
Raw Material Sourcing
The raw materials for fish meal production are typically sourced from the by-products of the fish processing industry. This includes fish trimmings, heads, tails, and bones. These by-products are often considered waste and would otherwise be discarded. However, by using these materials to produce fish meal, the industry is able to reduce waste and create a valuable product. The quality of the raw materials used in fish meal production is important, as it can affect the nutritional value and quality of the finished product. Therefore, it is important for fish meal plants to have a reliable and consistent source of high-quality raw materials.
Types of Fish Meal Plants

Fish meal plants are industrial facilities that process fish into fish meal, a valuable ingredient used in animal feed, fertilizers, and other products. There are two main types of fish meal plants: wet processing plants and dry processing plants.
Wet Processing Plants
Wet processing plants are designed to process whole fish or fish waste with high moisture content. These plants use water to extract fish oil and fish meal from the raw material. The process typically involves cooking, pressing, and drying the fish to remove water and produce a high-quality fish meal.
Wet processing plants can handle a wide range of fish species, including oily fish such as salmon and herring, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These plants are also capable of processing fish waste, such as heads, tails, and guts, which can be a valuable source of protein and other nutrients.
Dry Processing Plants
Dry processing plants are designed to process fish that have already been processed and have a low moisture content. These plants use heat and mechanical processing to extract fish oil and fish meal from the raw material. The process typically involves grinding, cooking, and pressing the fish to produce a high-quality fish meal.
Dry processing plants are typically used to process fish by-products, such as fish meal and fish oil, which are derived from fish that have been processed for human consumption. These plants are also used to process fish waste, such as fish bones and skin, which can be a valuable source of protein and other nutrients.
In summary, wet processing plants and dry processing plants are two main types of fish meal plants that differ in their processing methods and the types of raw materials they can handle. Both types of plants play an important role in the production of fish meal, a valuable ingredient used in a variety of products.
Key Equipment in Fish Meal Plants
Fish meal plants are equipped with several machines and equipment that are crucial to the production of high-quality fish meal. In this section, we will discuss the key equipment that is commonly used in fish meal plants.
Cookers
Cookers are one of the most important pieces of equipment in fish meal plants. They are used to cook and sterilize the fish before it is pressed to extract the oil and water. Cookers are typically large, cylindrical vessels that are heated by steam. The fish is loaded into the cooker, and steam is injected to raise the temperature to around 95°C. The fish is then held at this temperature for a set amount of time to ensure that it is fully cooked and sterilized.
Presses
Presses are used to separate the fish solids from the liquid. The cooked fish is loaded into a press, which applies pressure to the fish to extract the oil and water. The solids left behind are then ground into a fine powder, which is the fish meal. There are several types of presses used in fish meal plants, including screw presses and hydraulic presses. The type of press used depends on the size of the plant and the amount of fish being processed.
Dryers
Dryers are used to remove the moisture from the fish meal. The fish meal is loaded into a dryer, which is typically a large, rotating drum. Hot air is blown through the drum, which dries the fish meal and removes the moisture. Once the fish meal is dry, it is cooled and then stored in silos until it is ready to be packaged.
In conclusion, cookers, presses, and dryers are the key equipment in fish meal plants. They are all crucial to the production of high-quality fish meal. Fish meal plants must ensure that their equipment is properly maintained and operated to ensure that the final product meets the required standards.
Nutritional Value of Fish Meal
Protein Content
Fish meal is a high-quality source of protein, containing up to 60-70% protein by weight. This makes it an excellent ingredient for animal feed, especially for livestock and aquaculture. The protein in fish meal is highly digestible, which means that animals can easily absorb and utilize it for growth and development.
Amino Acid Profile
Fish meal is also a rich source of essential amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. These include lysine, methionine, cysteine, and tryptophan, among others. The amino acid profile of fish meal is well-balanced, which means that it can provide all the essential amino acids that animals need for optimal growth and health.
In addition to protein and amino acids, fish meal also contains other important nutrients such as minerals, vitamins, and omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients can help improve the overall health and well-being of animals that consume fish meal as part of their diet.
Overall, fish meal is a valuable ingredient for animal feed due to its high nutritional value and digestibility. It can help support the growth and development of livestock and aquaculture, and improve the quality of animal products such as meat, milk, and eggs.
Quality Control and Standards
Sampling Methods
Sampling methods play a significant role in ensuring that the quality of fish meal produced in a plant is up to standard. In most fish meal plants, samples are taken at various stages of the production process, including raw materials, intermediate products, and finished products. The samples are then analyzed in the laboratory to determine their quality parameters, such as protein content, fat content, and moisture content.
To ensure that the samples are representative of the entire batch, the sampling methods used should be standardized and consistent. The samples should be taken randomly from different parts of the batch and mixed thoroughly to obtain a homogeneous sample. The sample size should also be adequate to ensure that the results obtained are accurate and reliable.
Quality Parameters
Fish meal is a valuable source of protein for animal feed, and its quality is dependent on several parameters. The quality parameters of fish meal include protein content, fat content, moisture content, ash content, and histamine content.
The protein content of fish meal is one of the most critical parameters, and it should be at least 60% to be considered of high quality. The fat content should be below 10%, and the moisture content should be below 10% to prevent spoilage.
In addition to the above parameters, fish meal should also be free from contaminants such as heavy metals, pesticides, and pathogens. The presence of these contaminants can affect the quality of the fish meal and pose a risk to the health of animals that consume it.
To ensure that the fish meal produced in a plant meets the required quality standards, it is essential to have a quality control system in place. The system should include regular testing of samples, adherence to standard operating procedures, and continuous monitoring of the production process.
Environmental Considerations
Emission Controls
Fish meal plants can produce significant amounts of air pollution, particularly from the combustion of fuel in boilers used to dry the fish. To minimize emissions, these plants should have effective emission controls in place, such as scrubbers and electrostatic precipitators. These devices can remove particulate matter and other pollutants from the exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere.
In addition to controlling emissions from boilers, fish meal plants should also consider the use of low-emission transportation methods for moving raw materials and finished products. Trucks and ships can produce significant amounts of air pollution, so using cleaner alternatives such as electric vehicles or biofuels can help reduce the environmental impact of these operations.
Waste Management
Fish meal plants generate significant amounts of waste, including fish offal, wastewater, and solid waste from processing operations. To minimize the environmental impact of this waste, plants should implement effective waste management practices.
One approach is to use anaerobic digestion to convert fish waste into biogas, which can be used as a fuel for boilers or other equipment. This can help reduce the amount of waste that needs to be disposed of, while also producing a renewable energy source.
Another important consideration is the disposal of wastewater. Fish meal plants should treat their wastewater to remove pollutants before releasing it into the environment. This can be done through a variety of methods, such as sedimentation, filtration, and biological treatment.
Overall, effective emission controls and waste management practices are essential for minimizing the environmental impact of fish meal plants. By implementing these measures, these facilities can help ensure that their operations are sustainable and environmentally responsible.
Fish Meal Plant Locations
Geographical Distribution
Fish meal plants are located in coastal areas around the world due to their reliance on fresh fish as a raw material. The largest producers of fish meal are Peru, Chile, and Denmark, with other notable producers including Norway, Iceland, and the United States. These countries have a long history of fishing and have developed infrastructure and expertise in the industry.
Siting Criteria
When selecting a location for a fish meal plant, several factors are considered. The proximity to fishing grounds is crucial since fresh fish must be transported to the plant quickly to prevent spoilage. The availability of water is also important since large amounts of water are required for processing. In addition, the plant must be located away from residential areas due to the strong odor that emanates from the process. Finally, the plant must have access to transportation infrastructure such as ports and highways to facilitate the export of the finished product.
Overall, the location of fish meal plants is determined by a combination of factors that balance the need for proximity to fishing grounds with the need for suitable infrastructure and facilities.
Market and Economics
Demand Drivers
The demand for fish meal plants is driven by the growing demand for protein-rich animal feed. Fish meal is a valuable source of protein and essential amino acids, making it an important ingredient in animal feed. The increasing demand for meat and dairy products, particularly in developing countries, is driving the demand for fish meal plants.
Another factor driving the demand for fish meal is the growing aquaculture industry. Fish meal is an important ingredient in fish feed, which is used to feed farmed fish. As the demand for farmed fish increases, so does the demand for fish meal.
Price Trends
The price of fish meal is influenced by a number of factors, including the availability of raw materials, production costs, and demand. In recent years, the price of fish meal has been volatile due to fluctuations in the supply of raw materials.
The price of fish meal is also affected by competition from other protein sources, such as soybean meal and meat and bone meal. As the price of these alternative protein sources fluctuates, so does the demand for fish meal.
Despite these challenges, the fish meal industry is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. The increasing demand for protein-rich animal feed, coupled with the growing aquaculture industry, is expected to drive the demand for fish meal plants.
Regulatory Framework
International Guidelines
Fish meal plants are subject to various international guidelines that regulate the production, processing, and trade of fish meal. The most prominent among these guidelines are the Code of Conduct for Responsible Fisheries (CCRF) and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Technical Guidelines for Responsible Fisheries. These guidelines provide a framework for sustainable and responsible fishery management, including the use of fish meal plants.
The CCRF emphasizes the need for sustainable management of fishery resources, and encourages the use of fish meal plants that comply with environmental and social standards. The FAO Technical Guidelines for Responsible Fisheries provide detailed recommendations on the design, construction, and operation of fish meal plants, including the use of best available techniques and practices to minimize environmental impacts.
Local Regulations
In addition to international guidelines, fish meal plants are also subject to local regulations that vary depending on the country and region. Local regulations may cover aspects such as environmental protection, occupational health and safety, and food safety.
For example, in the United States, fish meal plants are subject to the Clean Water Act, which regulates the discharge of pollutants into waterways. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) also sets standards for worker safety and health in fish meal plants.
In Norway, fish meal plants must comply with strict environmental regulations, including limits on emissions of nitrogen and phosphorus. In addition, the Norwegian Food Safety Authority sets requirements for the quality and safety of fish meal products.
Overall, compliance with international guidelines and local regulations is essential for the sustainable and responsible operation of fish meal plants. By adhering to these guidelines and regulations, fish meal plants can minimize their environmental impact and ensure the safety and quality of their products.
Technological Advancements
Automation
Fish meal plants have seen significant advancements in automation technology in recent years. Automated systems have been introduced to handle the processing of fish, from the initial stages of sorting and cleaning to the final stages of packaging and shipping. These systems can significantly reduce the need for manual labor, which can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
One example of automation technology is the use of computer vision systems to sort fish. These systems use cameras and machine learning algorithms to recognize and sort fish based on various criteria such as size and species. This can greatly reduce the time and labor required for manual sorting.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is another area where fish meal plants have made significant advancements. The use of energy-efficient equipment and processes can help reduce energy consumption and lower operating costs. For example, some plants have implemented heat recovery systems to capture waste heat from various processes and use it to preheat water or air.
Another example is the use of high-efficiency motors and variable frequency drives (VFDs) to regulate the speed of motors and reduce energy consumption. These technologies can be applied to various processes such as conveyors, pumps, and fans.
Overall, these technological advancements in automation and energy efficiency have allowed fish meal plants to operate more efficiently and sustainably. By reducing the need for manual labor and lowering energy consumption, these advancements can help reduce costs and improve the bottom line.
Challenges and Risks
Resource Overexploitation
Fish meal plants rely heavily on the availability of fish as their primary raw material. However, overexploitation of fish stocks is a significant challenge that poses a risk to the sustainability of fish meal production. The demand for fish meal has led to overfishing in some regions, which can result in the depletion of fish populations. This can have a severe impact on the ecosystem and the livelihoods of people who depend on fishing.
To mitigate this risk, fish meal plants must ensure that they source their raw materials from sustainable sources. They can work with fishery management organizations to ensure that the fish stocks are harvested responsibly and that the ecosystem is not damaged.
Operational Hazards
Fish meal plants involve several operational hazards that can pose a risk to workers and the environment. The production process involves handling large quantities of fish, which can result in unpleasant odors and the release of hazardous gases. The handling of fish waste can also lead to the release of pollutants into the environment.
To mitigate these risks, fish meal plants must ensure that they have appropriate safety measures in place. This can include the use of protective equipment, proper ventilation systems, and waste management protocols. Additionally, regular training and monitoring can help to prevent accidents and ensure that the plant operates safely.
In conclusion, fish meal plants face several challenges and risks that must be addressed to ensure their sustainability. By sourcing their raw materials responsibly and implementing appropriate safety measures, fish meal plants can operate safely and contribute to the production of a valuable protein source for animal feed.