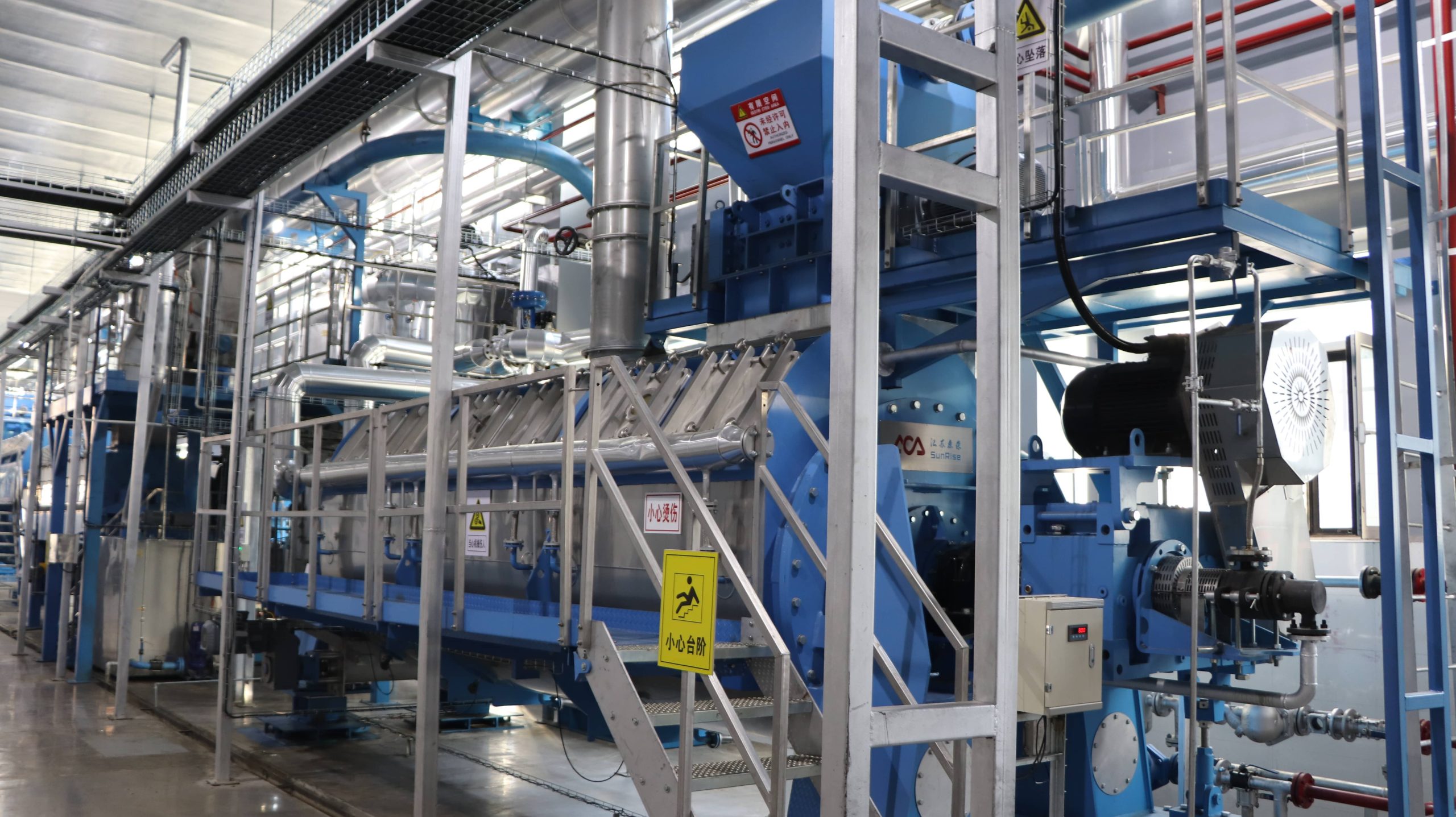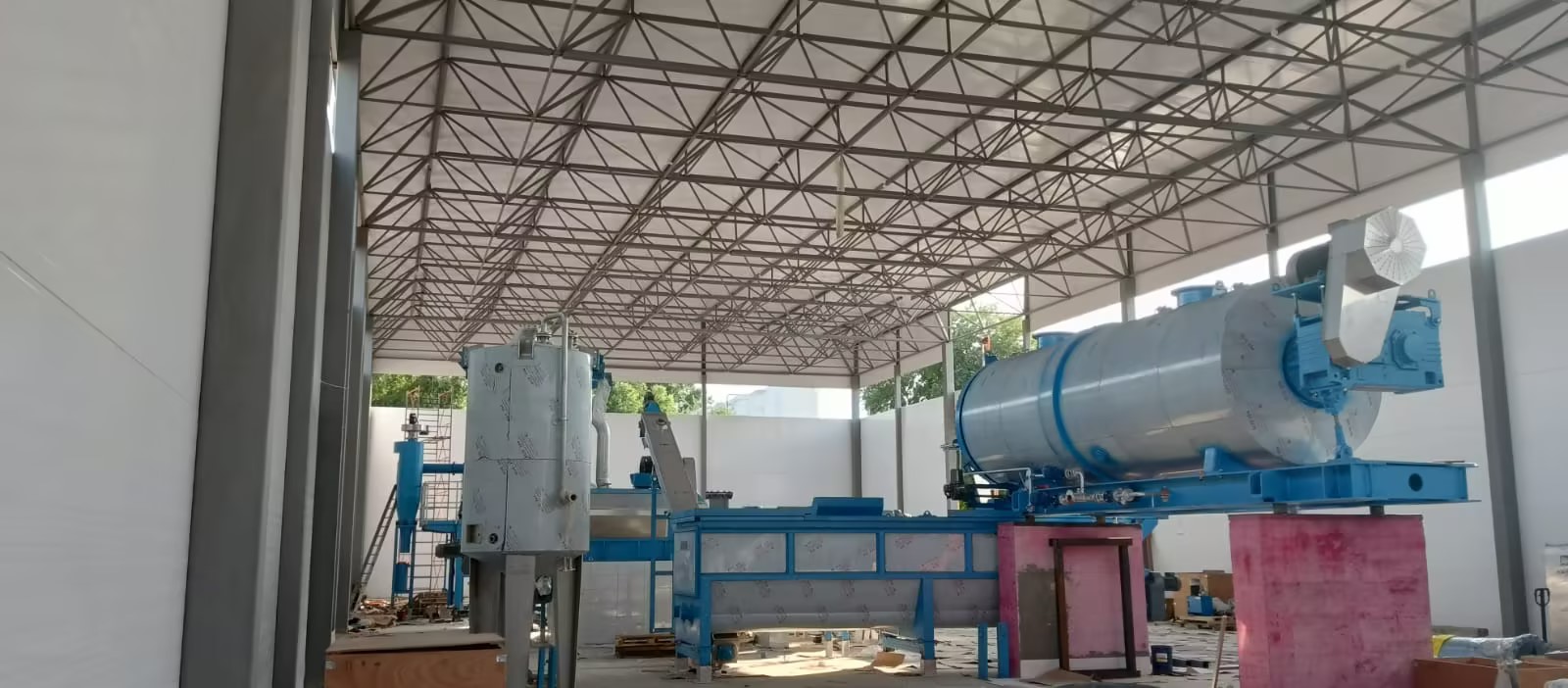
What is Animal By-Product Rendering: A Sustainable Solution
What is Animal By-Product Rendering: A Sustainable Solution
Animal by-product rendering is a transformative process that converts discarded animal byproducts into valuable resources. This metamorphosis unfolds within specialized rendering plants, where the animal remnants undergo a meticulous cooking process with the aid of water and steam, ultimately yielding a prized product known as meat and bone meal (MBM).
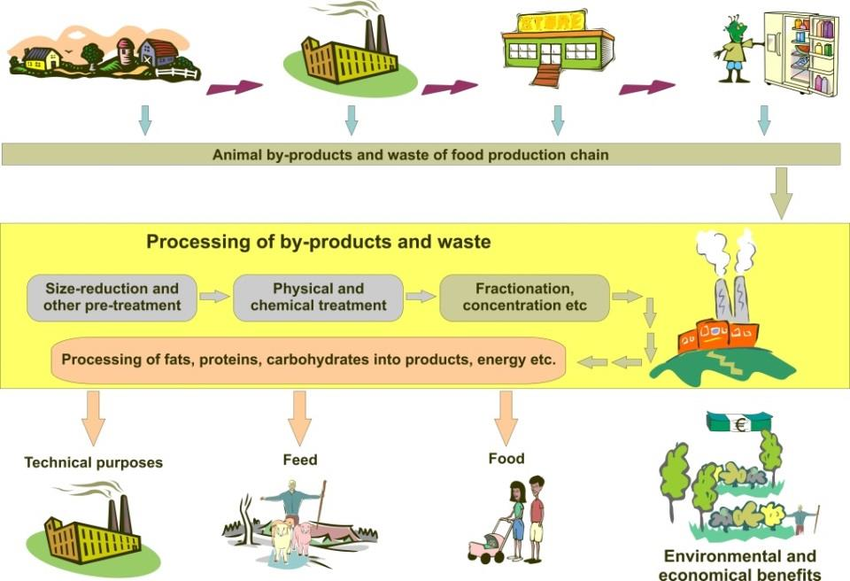
The primary objective of by-product rendering is to reclaim valuable nutrients from these materials, which can then be repurposed in various applications, including animal feed for pets and livestock. Beyond its economic benefits, by-product rendering holds significant environmental advantages, notably in reducing the volume of waste destined for landfills.
Rendering facilities are strategically positioned in proximity to farms, slaughterhouses, and processing facilities. These establishments are equipped with substantial storage capacities, enabling them to efficiently receive and process sizable shipments from these collaborating entities on a regular basis.
Where Does Rendering Come From?
Rendering as a process has historical roots dating back hundreds of years. It originated as a method for repurposing animal by-products, waste materials, and inedible parts of animals into useful products. Here’s a brief overview of the historical origins and development of rendering:
The Ancient Origins of Animal Fat Rendering and By-Product Utilization
The practice of rendering animal fats and utilizing animal by-products can be traced back to ancient civilizations. In cultures around the world, people discovered ways to extract fats and make use of animal parts that were not suitable for direct consumption.
Medieval Europe: The Formalization of Rendering and the Valorization of Tallow
Rendering became more formalized in medieval Europe, where it was often conducted in small-scale operations by individuals or small communities. Tallow (rendered animal fat) was a valuable commodity used for lighting lamps and making soap.
The Industrial Revolution’s Impact on Rendering: Evolution into a Recognizable Industry
The Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries brought significant changes to rendering. Advancements in technology and transportation allowed for the expansion of rendering facilities and the processing of larger quantities of animal by-products. This period saw the emergence of the rendering industry as a recognizable entity.
Modern Rendering Facilities: Pioneers of Technology, Sustainability, and Resource Management
Today, rendering facilities have evolved into sophisticated operations that employ advanced technology, strict quality control measures, and compliance with environmental regulations. They play a crucial role in managing organic waste materials, preserving resources, and contributing to various industries, including agriculture, food production, pet care, and biofuels.
The development of rendering reflects society’s historical need to minimize waste and efficiently use all parts of animals for various purposes. Over time, the industry has evolved to meet changing demands and regulatory requirements while continuing to find innovative ways to extract value from animal by-products. Modern rendering practices prioritize sustainability, biosecurity, and environmental responsibility while continuing to support a wide range of industries through the recovery of valuable resources.
Expanding Horizons in Agriculture and Meat Production Industries
As of my last knowledge update in September 2021, agriculture and meat production were indeed expanding industries in many parts of the world. However, it’s important to note that the status of these industries can change due to various factors, including shifts in consumer preferences, economic conditions, environmental concerns, and government policies. Here are some key points regarding the expansion of agriculture and meat production:
Growing Global Population and Rising Middle-Class Appetite: The Surge in Meat Demand
The world’s population continues to grow, which increases the demand for food, including meat products. As more people enter the middle class, their dietary preferences often include a greater consumption of animal protein, driving demand for meat.
Economic Development and Dietary Choices: A Shift Towards Protein-Rich Diets with Increased Meat Consumption
As economies develop, people tend to have higher incomes, allowing them to afford a more diverse and protein-rich diet that often includes more meat and animal products.
Emerging Markets Drive Agricultural and Meat Production Growth to Meet Escalating Food Demand
Emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America have seen significant growth in both agriculture and meat production as they modernize their farming practices and infrastructure to meet the rising demand for food.

Balancing Growth and Sustainability in Agriculture and Meat Production
While expansion continues, there is growing awareness of the environmental impact of agriculture and meat production, particularly related to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water usage. This has led to increased emphasis on sustainable practices and alternative protein sources, such as plant-based and cultured meats.
It’s essential to keep in mind that the dynamics of agriculture and meat production can vary greatly by region and country, and they are subject to ongoing changes and developments. Additionally, discussions about sustainability, animal welfare, and alternative protein sources are influencing the direction of these industries. Therefore, the expansion of agriculture and meat production should be considered within the broader context of evolving consumer preferences and global challenges.
Animal By-Products: Versatile Contributors to Multiple Industries and Products
Animal by-products indeed play a pivotal role across a broad spectrum of industries and products. These materials, often originating from animal processing for food or other purposes, undergo repurposing to minimize waste and make valuable contributions to various sectors. Here are several examples of industries and products that benefit from the utilization of animal by-products:
– Animal Feed
Among the most prevalent applications, animal by-products feature prominently in animal feed formulations. Ingredients like meat and bone meal, blood meal, and feather meal serve as crucial sources of protein and essential nutrients for livestock, poultry, and aquaculture.
– Pet Food
The production of pet food, including formulations for dogs and cats, incorporates animal by-products as nutritious and cost-effective ingredients, contributing to both dry and wet pet food varieties.
– Fertilizers
Certain animal by-products, including bone meal and blood meal, contribute to fertilizer production by providing valuable nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen, essential for enhancing plant growth.
– Pharmaceuticals
Collagen, a protein derived from animal connective tissues, finds application in pharmaceutical and medical sectors. It appears in various products, including gelatin capsules, wound dressings, and dietary supplements.
– Cosmetics
Collagen and other animal-derived components are featured in cosmetics and skincare products, known for their moisturizing and anti-aging properties, enriching the realm of personal care.
It is crucial to emphasize that the use of animal by-products is subject to regulatory oversight, and its application may vary depending on regional and national regulations. Furthermore, ethical and sustainability considerations exert a growing influence on the sourcing and utilization of animal-derived materials in various industries. Some sectors are exploring alternative options, such as plant-based or synthetic alternatives, to reduce reliance on animal by-products.

Animal By-Products Rendering Preserves The Environment
Animal by-products rendering can contribute to environmental preservation and sustainability in several ways:
Rendering: Transforming Organic Waste into Valuable Resources and Reducing Environmental Impact
Rendering reduces the volume of organic waste materials, including animal by-products, by breaking them down into valuable products like fats and proteins. This reduction in waste volume can significantly decrease the need for landfill space, reducing the environmental impact associated with landfilling organic waste.
Rendering Unlocks Valuable Resources from Animal By-Products, Fostering Resource Efficiency across Industries
Rendering extracts valuable resources from animal by-products, such as fats, proteins, and minerals. These recovered materials can be used in various industries, including animal feed, biodiesel production, and cosmetics, reducing the need for virgin resources and promoting resource efficiency.
Rendering: A Sustainable Solution to Mitigate Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Landfills
Rendering can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with organic waste decomposition in landfills. When organic materials decompose in landfills, they produce methane, a potent greenhouse gas. By rendering these materials, methane emissions are minimized, contributing to climate change mitigation.
Rendering Facilities and Water Management: Safeguarding Local Water and Ecosystems
Rendering facilities often include water treatment processes to manage wastewater and reduce the potential for water pollution. This helps protect local water bodies and ecosystems.
While rendering has numerous environmental benefits, it’s important to note that the industry also faces environmental challenges, such as the energy and water consumption associated with processing. To enhance sustainability, rendering facilities may adopt energy-efficient technologies, water recycling systems, and other eco-friendly practices. Additionally, ongoing research and innovation in rendering are aimed at reducing its environmental footprint further.
CONCLUSION
The rendering industry’s adherence to strict regulations and its commitment to compliance further ensure that rendering practices prioritize environmental protection and public health. As sustainability and resource efficiency continue to be paramount concerns, rendering facilities are likely to adopt even more eco-friendly technologies and practices, further reducing their environmental footprint.
In conclusion, animal by-product rendering plays a significant role in preserving the environment through waste reduction, resource recovery, greenhouse gas reduction, biosecurity, odor control, energy generation, conservation of natural resources, and reduced water pollution. By efficiently processing organic waste materials, rendering contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally responsible approach to waste management.



